

Without enzymes the larger food molecules would not be absorbed into the body through the lining of the small intestine as they cant pass though. They effectively act like scissors cutting up the large molecules. The break down large indigestible molecules into smaller digestible molecules. This mean that even when there is a higher substrate concentration, the activity will remain the same as there are not enough enzymes to break down the substrate that is available.Įnzymes work in the digestive system to help us digest food. However, when an enzyme becomes saturated, no more substrates can fit at any one time even though there is plenty of substrate available. When the concentration of the substrate increases, the rate of enzyme activity increases too. These are the conditions in which the enzyme would work best in.Įnzymes will work best if there is a lot of available substrate. This graph suggests that the optimum pH for: This graph suggests that the optimum temperature for this enzyme is around 70 degrees.Į.g. Different enzymes have different optimum temperatures and pH values.Į.g. Effects of Temperature Substrate Concentration & p Hįactors that affect the rate of a reaction include:Īll enzymes work best at only one particular temperature and pH: this is called the optimum. The substrate will no longer fit in the active site, therefore no products can be created.
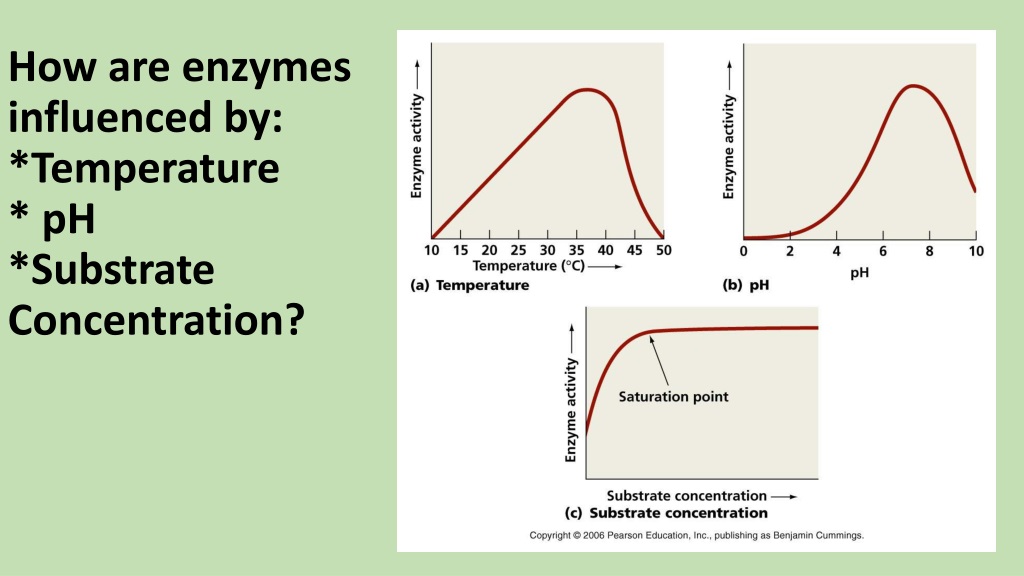
When this happens the enzyme is denatured.īut if it becomes denatured, it will look more like this: This affects the shape of the active site and means that the enzyme will no longer work. If the temperature and pH changes sufficiently beyond an enzyme’s optimum, the shape of the enzyme irreversibly changes.

Cells are the basic building blocks of all living organisms.



 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
